Myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) represents a bunch of inflammatory illnesses, together with polycythemia vera (PV), important thrombocythemia (ET), and first myelofibrosis (PMF). MPNs are linked to hematologic malignancies and are characterised by clonal outgrowth of hematopoietic cells with an acquired mutation in JAK2.
A number of research have proven that the Mediterranean eating regimen positively impacts illnesses related to power subclinical irritation. Along with the Mediterranean eating regimen, the intestine microbiome additionally performs an important position in bettering hematologic issues.
A brand new research printed to the medRxiv* preprint server assesses the feasibility of an education-focused Mediterranean eating regimen intervention amongst MPN sufferers.
 Examine: The NUTRIENT Trial (NUTRitional Intervention amongst myEloproliferative Neoplasms): Feasibility Part. Picture Credit score: Antonina Vlasova / Shutterstock.com
Examine: The NUTRIENT Trial (NUTRitional Intervention amongst myEloproliferative Neoplasms): Feasibility Part. Picture Credit score: Antonina Vlasova / Shutterstock.com

 *Essential discover: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific stories that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information medical apply/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
*Essential discover: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific stories that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information medical apply/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
Background
Scientific manifestations of MPN embody irregular blood counts, thrombosis, and transformation to acute leukemia. One of many key attribute options of MPN is elevated plasma cytokines.
Persistent irritation results in irregular blood depend. Though JAK inhibitors alleviate MPN signs, these medicine are related to sure dangers, akin to immunosuppression, pores and skin most cancers, and weight achieve.
The current Nationwide Complete Most cancers Community (NCCN) pointers for MPN proposed a number of interventions to scale back symptom burden, no matter the prognosis scoring class.
Since many MPN sufferers don’t meet the factors for a cytoreductive agent, their signs are maintained with out particular interventions. Because of this, the standard of life of those sufferers is adversely affected as a result of lack of ability to restrict illness development.
Life-style modification, primarily by means of eating regimen, can cut back irritation. For instance, a nutritious diet excessive in anti-inflammatory brokers can enhance symptom burden amongst MPN sufferers. Adherence to this sort of eating regimen can lower irritation and considerably delay or forestall illness development.
The Mediterranean eating regimen is a primarily plant-based eating regimen, which is related to the consumption of nuts, further virgin olive oil (EVOO), greens, fish, fruits, legumes, and complete grain merchandise. Controlling irritation by means of vitamin is a low-risk therapeutic strategy to mitigate the burden of signs for MPN sufferers.
Concerning the research
The first goal of the present research was to find out the willingness of MPN sufferers to interact in dietary schooling to handle symptom burden. Individuals had been randomly assigned to both a regular U.S. Dietary Pointers for Individuals (USDA) group or Mediterranean eating regimen group. Each teams obtained separate however equal schooling by means of written dietary sources and registered dietician counseling.
Sufferers had been adopted for adherence, feasibility, and symptom burden assessments. To discover modifications within the intestine microbiome and inflammatory biomarkers, organic samples had been collected at 4 distinct time factors all through the 15-week research interval.
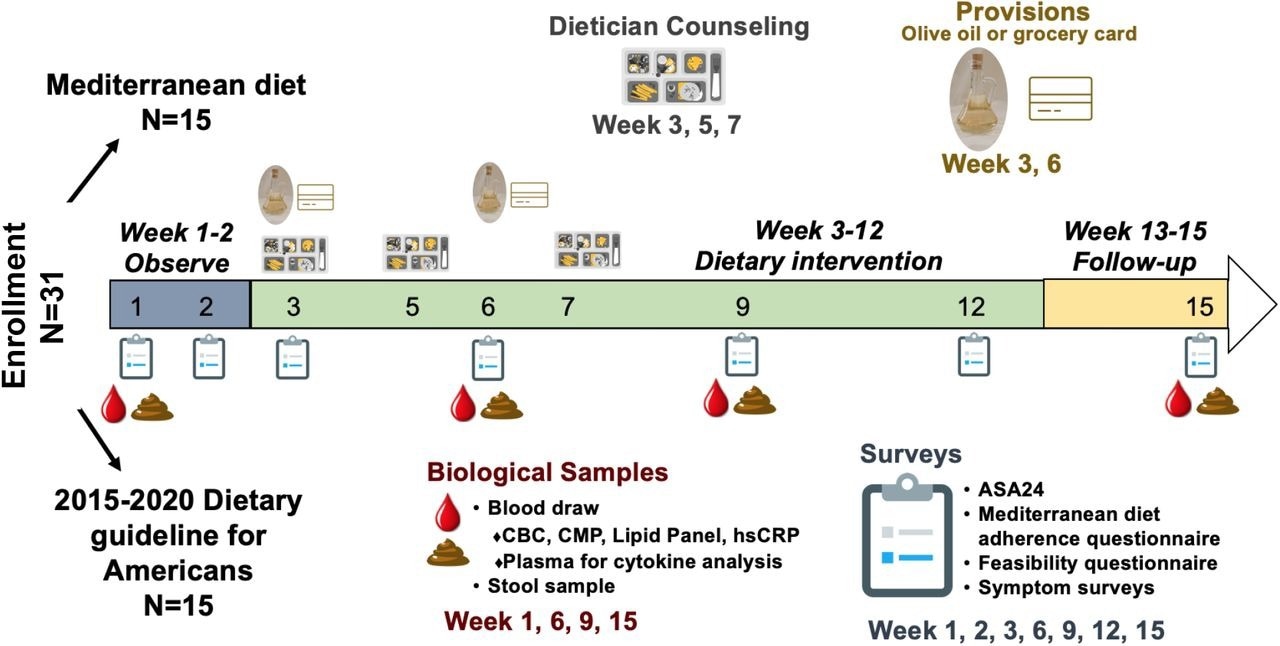
NUTRIENT research design.
Examine findings
MPN sufferers discovered the Mediterranean eating regimen program equally simple to observe as a program primarily based on the U.S. Pointers for Individuals. Over 80% of individuals within the Mediterranean eating regimen group might keep good adherence all through the intervention interval as in comparison with lower than 50% within the USDA group. This serves as proof that, with correct dietician counseling and written curriculum, MPN sufferers can feasibly undertake a Mediterranean eating regimen.
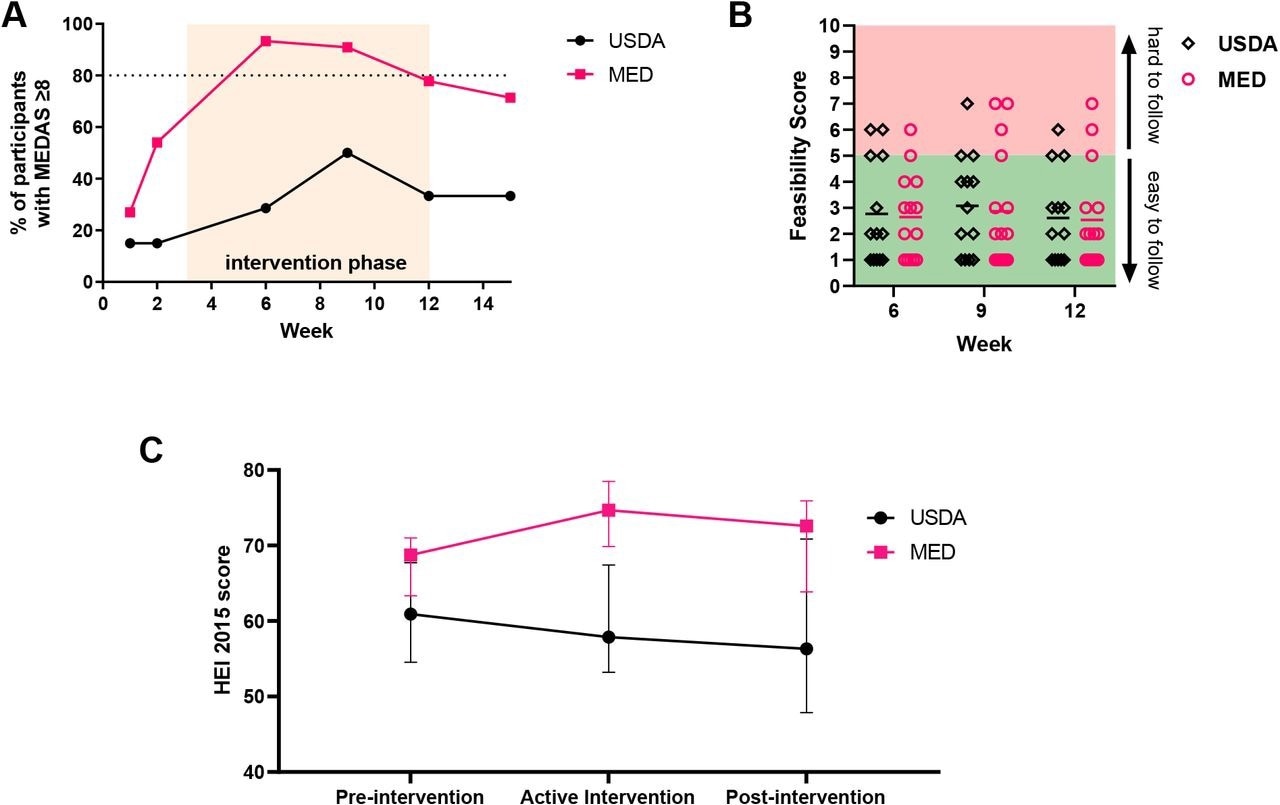
MPN sufferers can undertake a Mediterranean consuming sample with dietician counseling and schooling. (A) Proportion of participant with MEDAS scores ≥8 at every time level with orange shaded space depicting the lively intervention interval (B) Participant responses to feasibility query throughout lively intervention interval (C) HEI-2015 was calculated from every 24 hour eating regimen recall, and scores for every participant had been averaged for the pre-intervention (weeks 1-2), lively intervention (weeks 3-12), and post-intervention (weeks 13-15) interval. Information proven represents median with interquartile vary.
In MPN, an essential purpose is to focus on signs, as signs can considerably have an effect on the affected person’s’ high quality of life. Within the USDA group, 31% of the cohort exhibited greater than a 50% discount within the MPN-Complete Symptom Rating (TSS) at 15 weeks, whereas 53% of the Mediterranean eating regimen group exhibited greater than a 50% discount within the MPN-TSS.
As in comparison with the USDA eating regimen, the Mediterranean eating regimen had a greater impact on assuaging MPN signs. The size of the eating regimen intervention and depth are essential components in assuaging MPN signs.
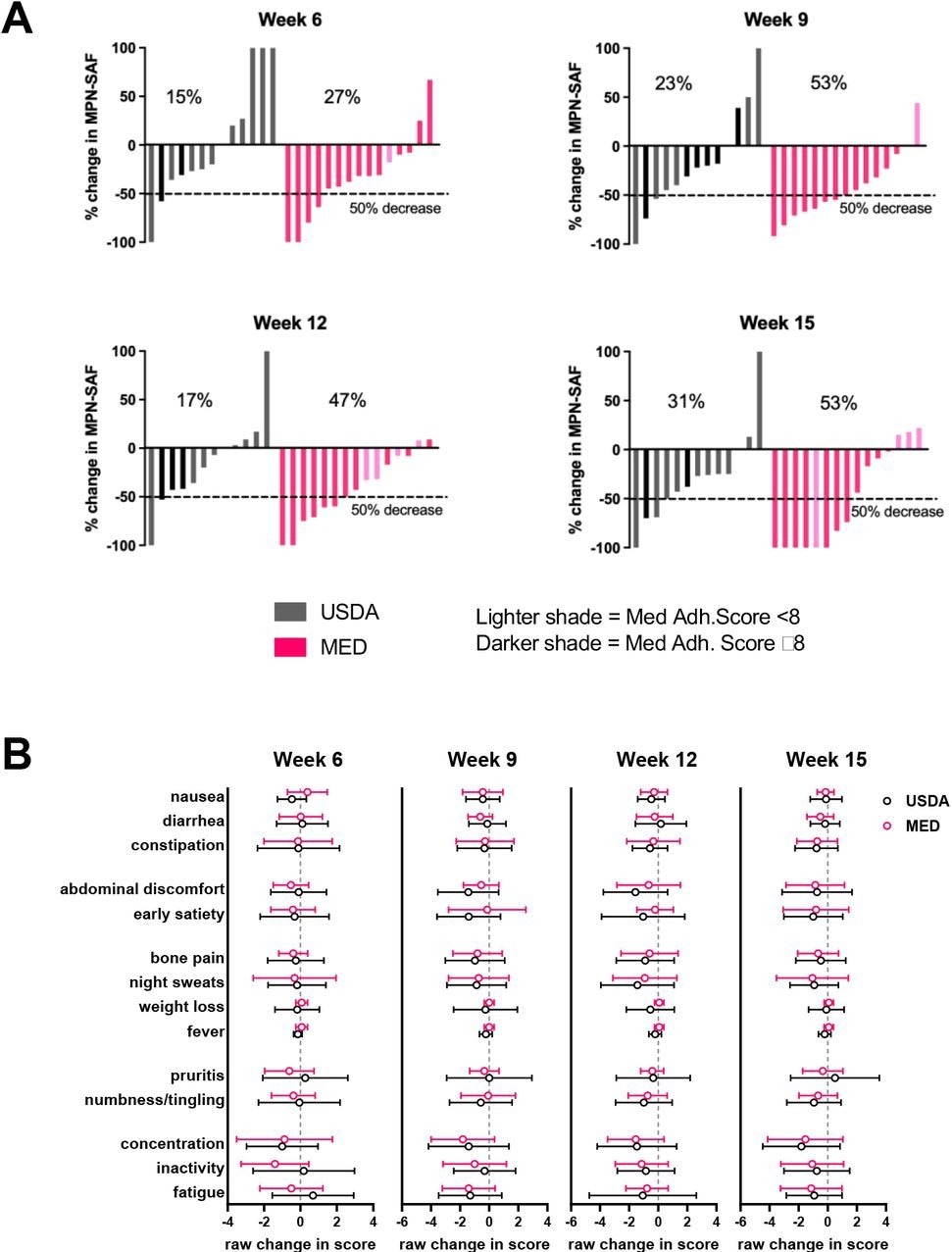
Modifications in symptom burden throughout research. (A) waterfall plots of share change in MPN-SAF (MPN-TSS) at every week in comparison with baseline (baseline outlined as common MPN-TSS of weeks 1 and a pair of) (B) Uncooked change in particular signs at every week in comparison with baseline (imply±SD).
Future outlook
Each diets investigated within the present research led to a discount in MPN symptom burden. Thus, these findings show {that a} 10-week intervention is adequate to detect a change in signs.
Sooner or later, an extended intervention interval is required to evaluate whether or not enhancements in signs proceed. An extended intervention interval would additionally assist detect individuals with delayed symptom enchancment.
The present evaluation highlights that MPN signs could stem from totally different root causes; subsequently, some signs change shortly in comparison with others. Because of the small pattern measurement, a lower within the inflammatory cytokines couldn’t be detected. Subsequently, future research with a bigger cohort are wanted to elucidate how diets affect inflammatory cytokine ranges.

 *Essential discover: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific stories that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information medical apply/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
*Essential discover: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific stories that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information medical apply/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
Journal reference:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Luque, M. F. L., Avelar-Barragan, J., Nguyen, H., et al. (2023) The NUTRIENT Trial (NUTRitional Intervention amongst myeloproliferative Neoplasms): Feasibility Part. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2023.05.09.23289740
